Abstract
Background:
Acalabrutinib is a more selective, second generation covalent binding Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor. It was designed with the intent to mitigate adverse events (AEs) associated with ibrutinib, such as bleeding and cardiovascular events. In the phase 3 trial that that led to acalabrutinib approval in the front line setting for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), 37% and 2% of patients who received acalabrutinib monotherapy experienced grade 1-2 or ≥3 bleeding events, respectively. Currently, there are no long term studies evaluating the incidence of bleeding events associated with acalabrutinib. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to assess the incidence of bleeding events, and risk factors associated with bleeding events for patients treated with acalabrutinib for hematologic malignancies.
Methods:
This was a single center retrospective study conducted at The Ohio State University. Patients were included if they were ≥18 years old, diagnosed with a hematologic malignancy, and initiated on acalabrutinib (monotherapy or combination therapy) between January 1, 2010 and August 31, 2019. The International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH) bleeding scale (no bleed, clinically non-relevant bleed, and clinically relevant/major bleed) and Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events V5.0 (CTCAE) were used to evaluate the grade and class of bleed events. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize demographic information and bleed events; univariable analysis was used to assess risk factors.
Results:
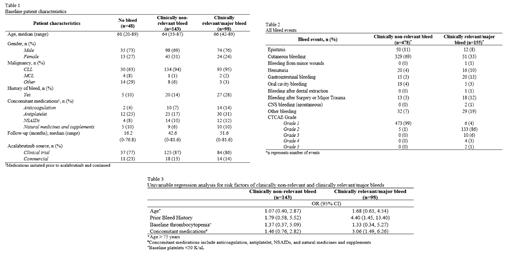
We analyzed 289 patients who received acalabrutinib for a hematologic malignancy. The main source of acalabrutinib was from clinical trials (85%) and the median acalabrutinib exposure time for all patients was 40.8 months (range: 0-81.6 months). 89% of patients had CLL, 2% had mantle cell lymphoma, and 9% had other non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Additionally, 18% of patients had a prior bleed history and 51% were continued on concomitant medications that increase bleeding (Table 1). There were a total of 241 (83%) patients who experienced at least one bleed event. Per ISTH categorization, 143 (59%) patients' most severe bleed event was clinically non-relevant and 98 (41%) patients' was clinically relevant/major; cutaneous bleeds were most common in both groups, 71% and 31%, respectively. Only 6% of patients had a major bleed, hence, clinically relevant and major bleeds were analyzed together for the purpose of this study.
There were a total of 633 bleed events that occurred in this study population; 76% were clinically-non relevant and only 3% (n=17) were CTCAE grade ≥3. Acalabrutinib was not discontinued or held for any clinically non-relevant bleeds, was discontinued for six (1%) clinically relevant/major bleeds, and held for 44 (7%) clinically relevant/major bleeds. Clinically relevant /major bleeds also resulted in discontinuations of concomitant anticoagulation and antiplatelet therapy in only 4% (n=24) of cases. 1263 procedures were identified and the incidence of clinically non-relevant and clinically relevant/major bleeds related to surgeries/procedures was 1% (n=12) and 1.3% (n=16), respectively.
10% of clinically non-relevant and 57% of clinically relevant/major bleeds led to hospitalizations, emergency room visits, or physician office visits; including two major CNS bleed events which resulted in death. The overall survival (OS) was not reached in the clinically non-relevant and clinically relevant/major bleed groups and was 14 months (95% CI 6-40) in the no bleed group (p=0.021). Univariate analysis showed that risk factors associated with a clinically relevant/major bleed included concomitant medications (OR 3.06, 95% CI 1.49-6.26) and prior bleed history (OR 4.40, 95% CI 1.45-13.40) (Table 3).
Conclusions:
Overall, our study had a long acalabrutinib exposure time and demonstrated a low incidence of grade ≥3 bleeds. There was also a low risk of bleeds related to procedures. The majority of bleeds were clinically non-relevant that did not result in significant treatment adjustments, hospitalizations, or death. This study identified prior bleed history and concomitant medications that increase bleeding as risk factors for bleeds and should be evaluated prior to starting acalabrutinib therapy. Our data supports acalabrutinib as a safe long-term treatment in regards to bleeds for patients with hematologic malignancies.
Wiczer: BTG Specialty Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Bhat: Beigene: Consultancy; Aptitude Health: Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Onclive: Honoraria. Byrd: Novartis, Trillium, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Pharmacyclics, Syndax: Consultancy, Honoraria; Newave: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Vincerx Pharmaceuticals: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Rogers: Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Acerta Pharma: Consultancy; Innate Pharma: Consultancy; ovartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Research Funding; AbbVie Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding. Woyach: AbbVie Inc, ArQule Inc, Janssen Biotech Inc, AstraZeneca, Beigene: Other: Advisory Committee; AbbVie Inc, ArQule Inc, AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, Janssen Biotech Inc, Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company,: Consultancy; AbbVie Inc, Loxo Oncology Inc, a wholly owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly & Company: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences Inc: Other: Data & Safety. Kittai: Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal